A Fine Example of an Overnight Trading Strategy: Rules, Backtest, Video Analysis
Mean reversion has worked very well on most Western stock indices for about four decades since the advent of futures trading. It has worked even better during the bull market after the financial crisis in 2008/09. Perhaps counterintuitive, long strategies have worked better in bear than bull markets. Please read our anatomy of a bear market to understand why long has performed better in bear markets. The same applies to our fine example of an overnight trading strategy that we cover in this article.
Overnight trading strategy example
One of the most popular mean reverting strategies is what we can label as “overnight trading”. If you are new to the concept we recommend two of our free articles about the subject:
- Night strategies trading (overnight edges/strategies)
- How do you do overnight trading? (How to make money overnight trading)
The main benefit of having trading strategies with such low exposure to the market is that the drawdown is lower. Big drawdowns are what make most traders quit at the wrong moments when the market turns around.
24-hour trading strategies
Before you continue reading, please consider having a look at the 3 24-hour trading strategies we offer as a bundle. They enter at the close of a trading day and sell at the close 24 hours later.
However, let’s return to our overnight trading strategy:
Overnight trading strategy – trading rules
[am4show have=’p2;p3;p58;p59;p130;p138;’ user_error=’Premium Post Access’ guest_error=’Premium Posts’]
- Calculate the absolute value of the % change from today’s close from yesterday’s close (c2c).
- Calculate a 25-day average of number 1.
- When SPY falls more than two times the number in number 2 from Close to Close (c2c), then go long at the close.
- Exit on next day’s close.
[/am4show]
If you want the Amibroker code for the strategy and the code for more than 200 other strategies (the code for all our free articles), you can order it here.
The strategy returns this equity curve on the S&P 500 (SPY):
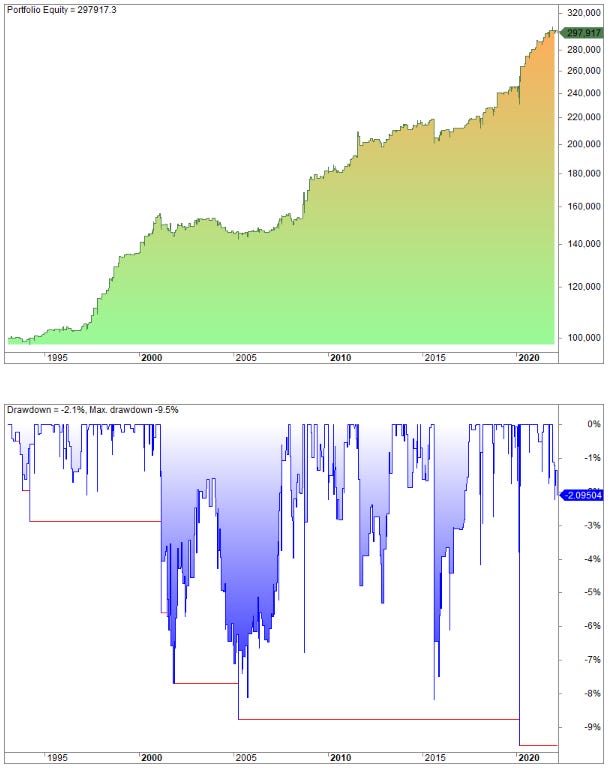
The average gain is 0.25%, the win rate is 59%, and the winners are 15% bigger than the average loser. If we avoid Thursdays the average return increases to 0.33.
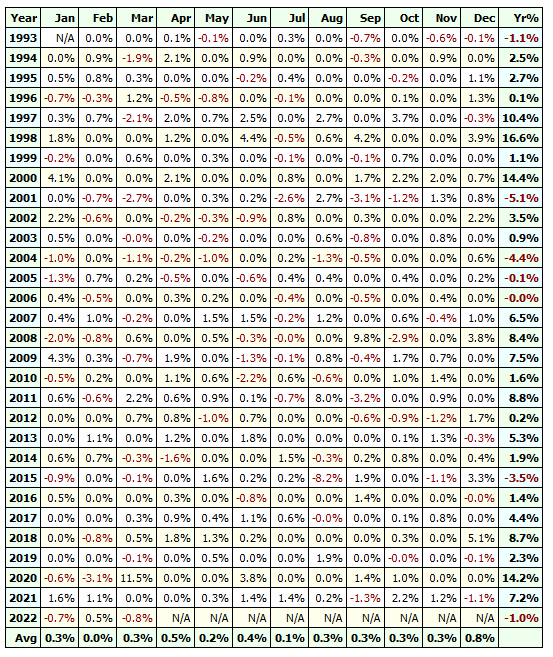
If we look at the annual returns it looks like this:
Does the strategy work on the short side?
[am4show have=’p2;p3;p58;p59;p130;p138;’ user_error=’Premium Post Access’ guest_error=’Premium Posts’]
If we increase the threshold to 2.5 times the average of 2c2 we get the following equity short:
[/am4show]
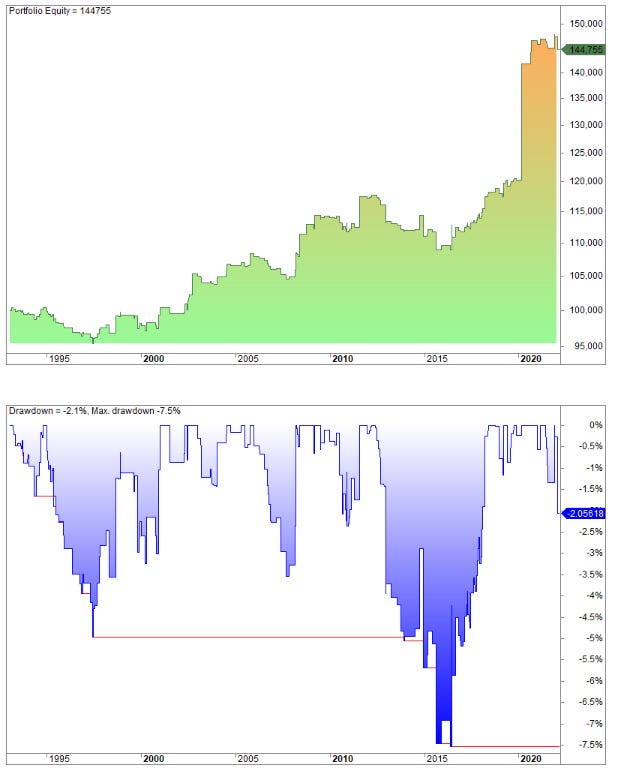
The average gain per trade is 0.19% but as you can see, the gains are pretty unpredictable.
FAQ:
Why has mean reversion been effective for several decades?
Mean reversion is a trading strategy based on the idea that asset prices tend to revert to their historical average over time. This approach has been successful in Western stock indices for about four decades, offering traders opportunities to capitalize on price movements returning to the mean.
Why do long strategies perform better in bear markets?
Long strategies often perform better in bear markets due to specific market dynamics. Understanding the anatomy of a bear market is crucial. The mean-reverting nature of certain strategies, including overnight trading, can be advantageous in both bear and bull markets.
What is the overnight trading strategy, and how does it work?
The overnight trading strategy is a mean-reverting approach with low exposure to the market. It involves calculating the absolute value of the percentage change from the current day’s close to the previous day’s close. By entering long positions when specific conditions are met, traders aim to capitalize on short-term mean-reverting price movements.
