Best Trading Strategies For Forex (Rules, Results, And Performance)
Introduction to Forex Trading:
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is the practice of buying and selling currencies in the global financial market for financial gains.
It is a decentralized marketplace where participants trade one currency for another, aiming to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. Forex trading is significant due to its immense liquidity and accessibility, enabling individuals, institutions, and businesses to engage in currency exchange for various purposes, including investments, international trade, and risk management.
Forex trading offers a low-bar entry for retail traders because of low margin requirements.
Having a specific trading strategy in Forex, preferably backtested, is essential for several reasons:
First, it provides a structured approach to decision-making, helping traders navigate the complexities of the market with a clear plan.
Second, it assists in managing risk by defining entry and exit points and setting stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Third, a well-defined strategy helps traders maintain discipline and emotional control, reducing the impact of impulsive decisions.
Ultimately, a trading strategy is crucial for achieving consistent and profitable outcomes in the Forex market.
Understanding Forex Market Basics
Understanding forex market basics is crucial for anyone looking to engage in foreign exchange trading. This knowledge encompasses three fundamental concepts: Currency Pairs, Exchange Rates, and Market Participants.
Currency Pairs form the foundation of forex trading. In this market, you don’t just trade one currency; instead, you deal with pairs of currencies. Each pair consists of two currencies, such as the EUR/USD or GBP/JPY. The first currency in the pair is known as the base currency, while the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate represents how much of the quote currency you need to buy one unit of the base currency. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.20, it means you need 1.20 US dollars to buy 1 Euro. These pairs are classified into three categories: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs, based on their liquidity and popularity.
Exchange Rates are at the core of forex trading. They represent the relative value of one currency compared to another. Exchange rates are not fixed; they fluctuate constantly due to various factors like economic data releases, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. Traders monitor these rates closely to make informed decisions on when to buy or sell currency pairs. Exchange rates can be quoted in two ways: direct and indirect. A direct quote expresses the domestic currency’s value in terms of a foreign currency, while an indirect quote expresses the foreign currency’s value in terms of the domestic currency.
Market Participants encompass a diverse group of individuals and institutions that contribute to the forex market’s liquidity and dynamism. These participants include central banks, commercial banks, hedge funds, multinational corporations, retail traders, and brokers. Central banks play a pivotal role in forex by implementing monetary policies and intervening in the market to stabilize their country’s currency. Commercial banks facilitate forex transactions for their clients and engage in speculative trading. Hedge funds and multinational corporations use forex to hedge against currency risk or profit from exchange rate movements. Retail traders, like individual investors, access the market through brokers and trade smaller volumes compared to institutions.
Forex is a zero-sum game: Always keep in mind that the forex markets are a zero-sum game. What you gain or lose, someone else must lose or gain. It’s all relative – one currency against another.
Thus, it doesn’t offer a tailwind like you get in stocks. If you invest in stocks it can snowball by compounding interest, but forex doesn’t offer anything like that. This is one of the reasons why we believe it’s much better to trade stocks than forex.
Importance of Having a Trading Strategy
The importance of having a trading strategy cannot be overstated. By plan we mean that you have specific trading rules that most likely have a positive expectancy over time. It serves as a blueprint.
Risk management is a fundamental component of any trading strategy. It involves assessing and mitigating potential losses to protect your capital. Effective risk management helps traders survive turbulent market conditions. The best way to manage risk is to trade many different strategies: different types, different time frames, different markets, and different market directions.
Consistency is key in trading. A well-defined strategy helps maintain a consistent approach, reducing the impact of impulsive decisions. Consistency leads to stability and better overall results.
Emotional control is critical for traders. Emotions like fear and greed can lead to impulsive actions, causing losses. A trading strategy helps traders stay disciplined and avoid making decisions based on emotions. If you are an mechanical and automated trader, you create a layer between you and the market, and thus you are less likely to make unnecessary trading mistakes based on biases.
Types of Forex Trading Strategies
There are plenty of ways to approach the forex market: mean reversion strategies, momentum, and trend, just to name the most obvious ones.
That said, we regard the forex market as perhaps the most difficult market to trade. Sadly, it’s also the market that most retail traders start with, most likely because they are undercapitalized and forex brokers offer very low margins, even up to 50:1. In a previous article we wrote about 12 reasons to avoid the forex market.
Let’s give you an example of a backtested trading strategy with specific trading rules. This is a trend following trading strategy.
As we have mentioned earlier, we strongly recommend backtesting. If you are unsure or uncertain what is is, please read our long backtesting guide with pros and cons.
The backtest is performed vis DXY – the USD index, but we trade EUR and USD.
The trading strategy is simple and has the following trading rules:
[am4show have=’p2;p3;p58;p59;p130;p138;’ user_error=’Premium Post Access’ guest_error=’Premium Posts’]
- When DXY is lower than it’s 30-week simple moving average, we buy spot euro.
- When DXY is higher than it’s 30-week simple moving average, we buy spot dollars.
[/am4show]
The result of the trading strategy can be seen in the equity curve below.
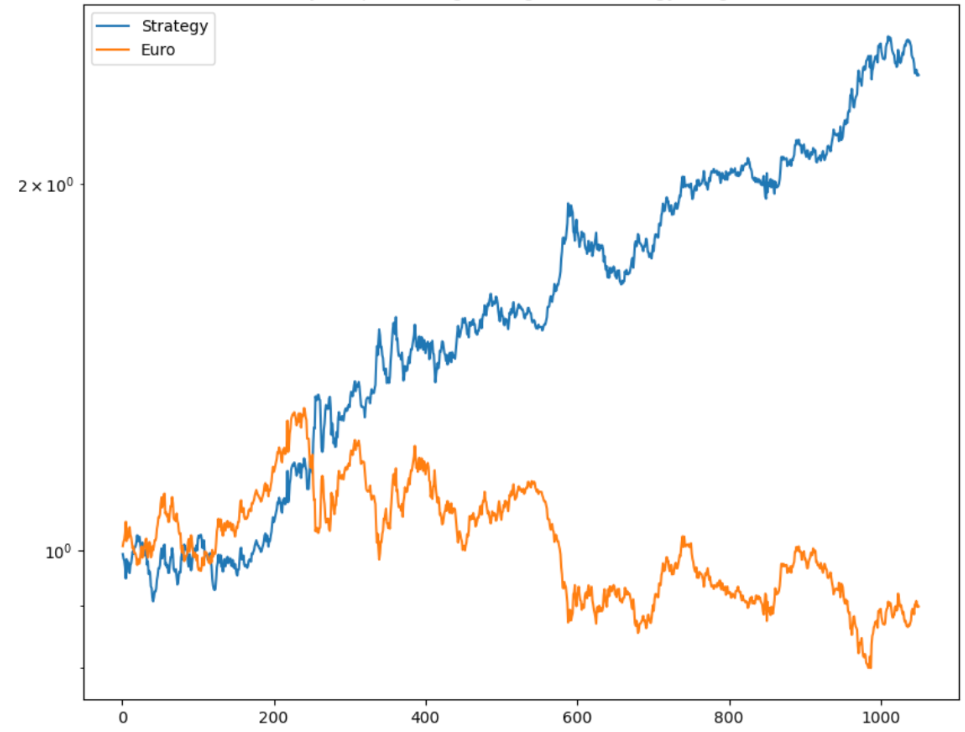
As you can see, such a simple trading strategy has worked well for a very long time (the backtest is from May 2003 until today). The forex strategy has its drawdowns, but new highs happen not long after a mild drawdown.
The CAGR is 4.55%. This won’t set the world on fire, but it’s still very good if you can use some kind of leverage. And the best part is that the results are completely independent and uncorrelated to the stock market, which makes it very good for strategy diversification.
But what if we change the value of the only parameter in this forex trading strategy? Does it work with other values, or is this strategy just a result of sheer luck and randomness?
There is only one way to find out, and that is via trading strategy optimization and evaluation to get more statistics and data to measure its performance.
We backtested the strategy performance ranging from values ranging from 3 to 200. Here are the compounded results:
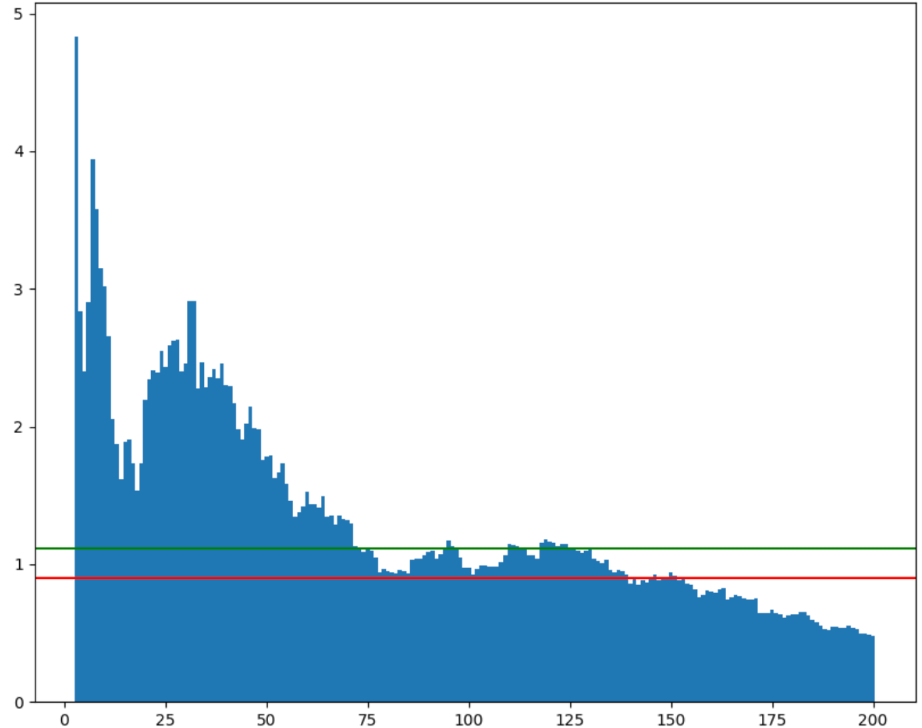
As you can see, the strategy performs well when the values are lower than 50. However, its peak performance is achieved when the values are on the short side – less than 10.
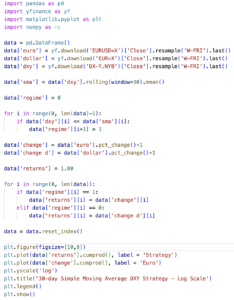
If you are a Python coder, we provide you with the full code here:
[am4show have=’p2;p3;p58;p59;p130;p138;’ user_error=’Premium Post Access’ guest_error=’Premium Posts’]
[/am4show]